1. 같은 종류의 원소 갯수 구하기 => HashMap 이용
2. 1번을 내림차순 정렬
3. 갯수가 많은 것부터 k개 고르기
✏️ Solution 1
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class 귤고르기 {
public static int solution(int k, int[] tangerine) {
int sum = 0; // 고를 귤의 개수
int cnt = 0; // 최솟값 카운트
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for(int num : tangerine) {
map.put(num, map.getOrDefault(num, 0)+1);
}
// System.out.println("map: " + map);
ArrayList<Integer> valueList = new ArrayList<>(map.values());
Collections.sort(valueList, Collections.reverseOrder());
// System.out.println(valueList);
for(int v : valueList) {
if (sum+v >= k) {
cnt++;
break;
} else {
sum += v;
cnt++;
}
}
return cnt;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(solution(6, new int[]{1, 3, 2, 5, 4, 5, 2, 3}));
System.out.println(solution(4, new int[]{1, 3, 2, 5, 4, 5, 2, 3}));
System.out.println(solution(2, new int[]{1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 3}));
}
}
2025.03.14 - [IT/Algorithm | Coding Test] - HashMap
HashMap
HashMap- 자바의 컬렉션 프레임워크 중 하나로, 키와 값의 쌍으로 데이터를 저장하는 자료구조- 해시 테이블을 기반으로 하며, 키를 해시 함수로 해시 코드로 변환하여 값을 저장하고 검색
iamsh.tistory.com
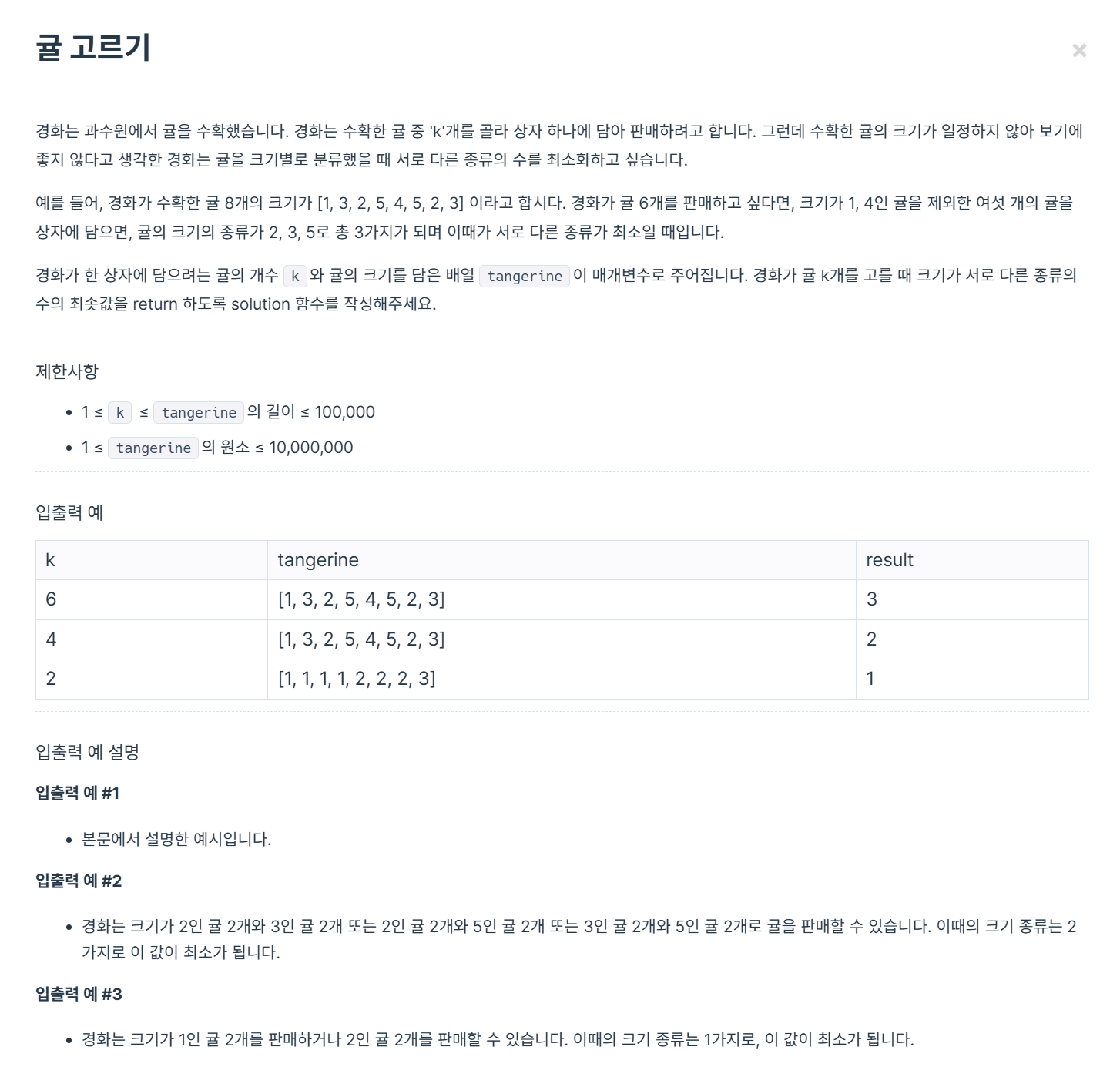
✍🏼 HashMap을 사용하여 귤의 개수 세기
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int num : tangerine) {
map.put(num, map.getOrDefault(num, 0) + 1);
}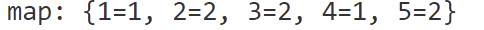
map.getOrDefault(num,0)+1 현재 귤의 개수 증가시키기
- map에서 키(num)에 해당하는 값을 가져오고, 값이 존재하지 않으면 기본값(0) 반환한다
- +1을 map에 저장하여 키(num)의 값을 1 증가시킨다.
✍🏼 HashMap의 값을 리스트로 변환하고 내림차순 정렬
<= 귤의 개수를 내림차순으로 "정렬"하기 위해 리스트를 사용한다.
ArrayList<Integer> valueList = new ArrayList<>(map.values());
Collections.sort(valueList, Collections.reverseOrder());
✏️ Solution 2
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
public class 귤고르기_2 {
public static int solution(int k, int[] tangerine) {
int answer = 0;
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for(int i : tangerine) {
map.put(i, map.getOrDefault(i,0)+1);
}
List<Integer> keyList = new ArrayList<>(map.keySet());
// System.out.println(keyList);
keyList.sort( (o1,o2) -> map.get(o2) - map.get(o1) );
// System.out.println(keyList);
for (Integer i : keyList) {
if (k <= 0) {
break;
}
answer++;
k -= map.get(i);
}
return answer;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(solution(6, new int[]{1, 3, 2, 5, 4, 5, 2, 3}));
System.out.println(solution(4, new int[]{1, 3, 2, 5, 4, 5, 2, 3}));
System.out.println(solution(2, new int[]{1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 3}));
}
}
✅ 리스트 정렬하는 코드
keyList.sort((o1, o2) -> map.get(o2) - map.get(o1));리스트를 value 기준으로 내림차순 정렬한다.
- map.get(o2) - map.get(o1)는 o2와 o1에 해당하는 값의 차이를 계산한다.
- 값이 양수이면 o2가 o1보다 앞에 오도록 정렬한다.
- 값이 큰 key가 앞에 오도록 내림차순으로 정렬한다
오름차순 정렬 => map.get(o1) - map.get(o2));
'IT > Algorithm | Coding Test' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [프로그래머스 12914] [Java] 멀리뛰기 (2) | 2025.03.17 |
|---|---|
| HashMap (0) | 2025.03.17 |
| [프로그래머스 12945] [Java] 피보나치 수 (0) | 2025.03.11 |
| [프로그래머스 12911] [Java] 다음 큰 숫자 (0) | 2025.03.01 |
| [프로그래머스 70129] [Java] 이진 변환 반복하기 (0) | 2025.02.27 |